Chapter 3: Introductory Chemistry for Biology
3.2. Atoms
Learning Objectives
By the end of this section, you will be able to:
- Discuss the relationships between matter, mass, elements, compounds, atoms, and subatomic particles.
- Distinguish between atomic number and mass number.
- Identify the key distinction between isotopes of the same element.
- Explain how electrons occupy electron shells and their contribution to an atom’s relative stability.
An atom is the smallest component of an element that retains all of the chemical properties of that element. For example, one hydrogen atom has all of the properties of the element hydrogen, such as it exists as a gas at room temperature, and it bonds with oxygen to create a water molecule. Hydrogen atoms cannot be broken down into anything smaller while still retaining the properties of hydrogen. If a hydrogen atom were broken down into subatomic particles, it would no longer have the properties of hydrogen.
All atoms contain protons, electrons, and neutrons (Figure 3.2.1). The only exception is hydrogen (H), which is made of one proton and one electron.
A proton is a positively charged particle that resides in the nucleus (the core of the atom) of an atom and has a mass of 1 and a charge of +1. An electron is a negatively charged particle that travels in the space around the nucleus. In other words, it resides outside of the nucleus. It has a negligible mass and has a charge of –1. Neutrons, like protons, reside in the nucleus of an atom. They have a mass of 1 and no charge. The positive (protons) and negative (electrons) charges balance each other in a neutral atom, which has a net zero charge.
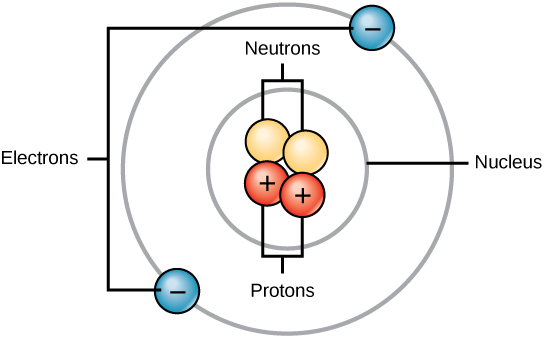
Since protons and neutrons each have a mass of 1, the mass of an atom is equal to the number of protons and neutrons of that atom. The number of electrons do not factor into the overall mass, since their mass is so small.
At the most basic level, all organisms are made of a combination of elements. An element is a substance whose atoms all have the same number of protons. They contain atoms that combine together to form molecules. In multicellular organisms, such as animals, molecules can interact to form cells that combine to form tissues, which make up organs. These combinations continue until entire multicellular organisms are formed.
Each element has its own unique properties. Each contains a different number of protons and neutrons, giving it its own atomic number and mass number. The atomic number of an element is equal to the number of protons that element contains. The mass number, or atomic mass, is the number of protons plus the number of neutrons of that element. Therefore, it is possible to determine the number of neutrons by subtracting the atomic number from the mass number.
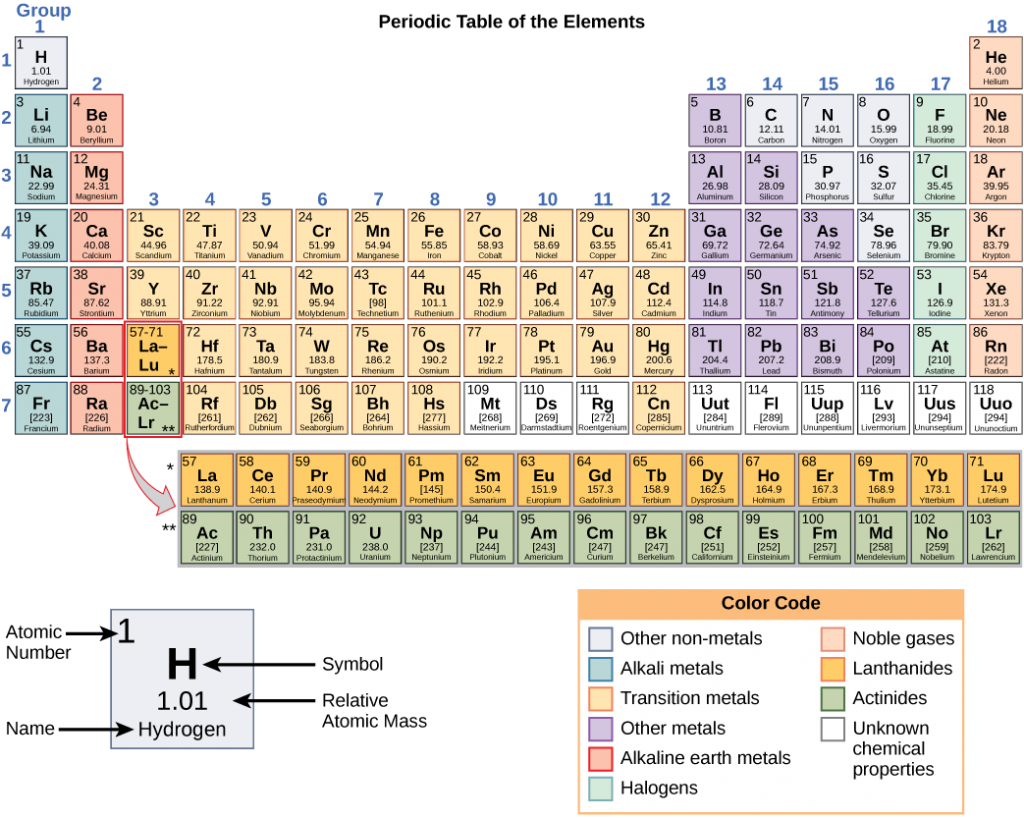
These numbers provide information about the elements and how they will react when combined. Different elements have different melting and boiling points, and are in different states (liquid, solid, or gas) at room temperature. They also combine in different ways. Some form specific types of bonds, whereas others do not. How they combine is based on the number of electrons present. Because of these characteristics, the elements are arranged into the periodic table of elements, a chart of the elements that includes the atomic number and relative atomic mass of each element. The periodic table also provides key information about the properties of elements (Figure 3.2.2) —often indicated by color-coding. The arrangement of the table also shows how the electrons in each element are organized and provides important details about how atoms will react with each other to form molecules.
Isotopes are different forms of the same element that have the same number of protons, but a different number of neutrons. Some elements, such as carbon, potassium, and uranium, have naturally occurring isotopes. Carbon-12, the most common isotope of carbon, contains six protons and six neutrons. Therefore, it has a mass number of 12 (six protons and six neutrons) and an atomic number of 6 (which makes it carbon). Carbon-14 contains six protons and eight neutrons. Therefore, it has a mass number of 14 (six protons and eight neutrons) and an atomic number of 6, meaning it is still the element carbon. These two alternate forms of carbon are isotopes. Some isotopes are unstable and will lose protons, other subatomic particles, or energy to form more stable elements. These are called radioactive isotopes or radioisotopes.
Electron distribution
How elements interact with one another depends on how their electrons are arranged and how many openings for electrons exist at the outermost region where electrons are present in an atom. Electrons exist at energy levels that form shells around the nucleus. The closest shell can hold up to two electrons. The closest shell to the nucleus is always filled first, before any other shell can be filled. Hydrogen has one electron; therefore, it has only one spot occupied within the lowest shell. Helium has two electrons; therefore, it can completely fill the lowest shell with its two electrons. If you look at the periodic table, you will see that hydrogen and helium are the only two elements in the first row. This is because they only have electrons in their first shell. Hydrogen and helium are the only two elements that have the lowest shell and no other shells.
The second and third energy levels can hold up to eight electrons. The eight electrons are arranged in four pairs and one position in each pair is filled with an electron before any pairs are completed.
Looking at the periodic table again (Figure 3.2.2), you will notice that there are seven rows. These rows correspond to the number of shells that the elements within that row have. The elements within a particular row have increasing numbers of electrons as the columns proceed from left to right. Although each element has the same number of shells, not all of the shells are completely filled with electrons. If you look at the second row of the periodic table, you will find lithium (Li), beryllium (Be), boron (B), carbon (C), nitrogen (N), oxygen (O), fluorine (F), and neon (Ne). These all have electrons that occupy only the first and second shells. Lithium has only one electron in its outermost shell, beryllium has two electrons, boron has three, and so on, until the entire shell is filled with eight electrons, as is the case with neon.
Evolution in Action
Carbon Dating: Carbon-14 (14C) is a naturally occurring radioisotope that is created in the atmosphere by cosmic rays. This is a continuous process, so more 14C is always being created. As a living organism develops, the relative level of 14C in its body is equal to the concentration of 14C in the atmosphere. When an organism dies, it is no longer ingesting 14C, so the ratio will decline. 14C decays to 14N by a process called beta decay; it gives off energy in this slow process.
After approximately 5,730 years, only one-half of the starting concentration of 14C will have been converted to 14N. The time it takes for half of the original concentration of an isotope to decay to its more stable form is called its half-life. Because the half-life of 14C is long, it is used to age formerly living objects, such as fossils. Using the ratio of the 14C concentration found in an object to the amount of 14C detected in the atmosphere, the amount of the isotope that has not yet decayed can be determined. Based on this amount, the age of the fossil can be calculated to about 50,000 years (Figure 3.2.3). Isotopes with longer half-lives, such as potassium-40, are used to calculate the ages of older fossils. Through the use of carbon dating, scientists can reconstruct the ecology and biogeography of organisms living within the past 50,000 years.

License and attributions:
-
- Concepts of Biology, 2013, Fowler, S. et al. License: CC BY 4.0. Located at https://openstax.org/books/concepts-biology/pages/2-1-the-building-blocks-of-molecules
